Frequency Inverter Failures: How to Prevent Unexpected Downtime and Protect Your Operation
25/08/2025

In modern industry, variable frequency drives (VFDs) are the heart of many technological processes. They are highly reliable devices, but like any equipment, they can fail. VFD failures can lead to unexpected downtime, significant production losses, and high costs. This article will focus on the five most common VFD failures and, most importantly, provide concrete steps on how to prevent them.
The 5 Most Common VFD Failures
- 1. Overheating of the Inverter: This is one of the most frequent causes of failure. It is often caused by a clogged cooling system, poor cabinet ventilation, or high ambient temperatures.
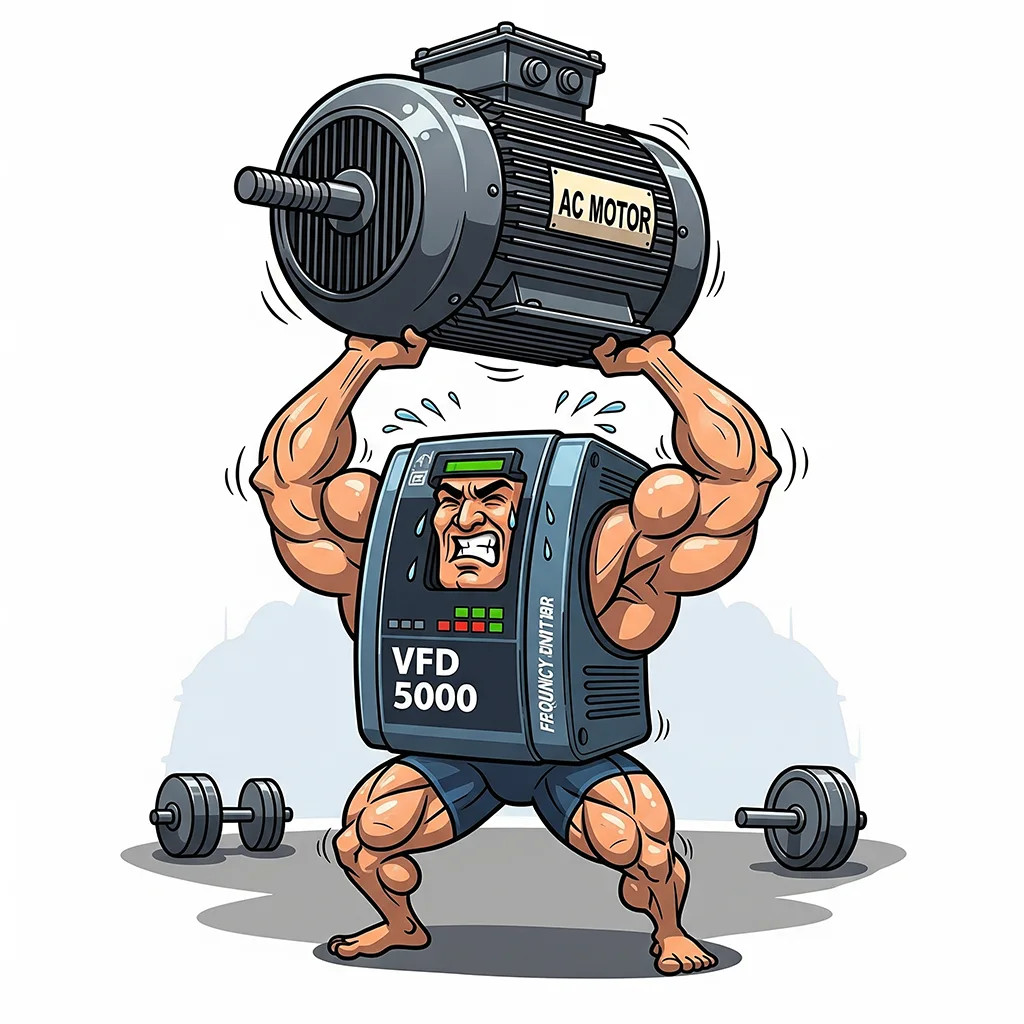

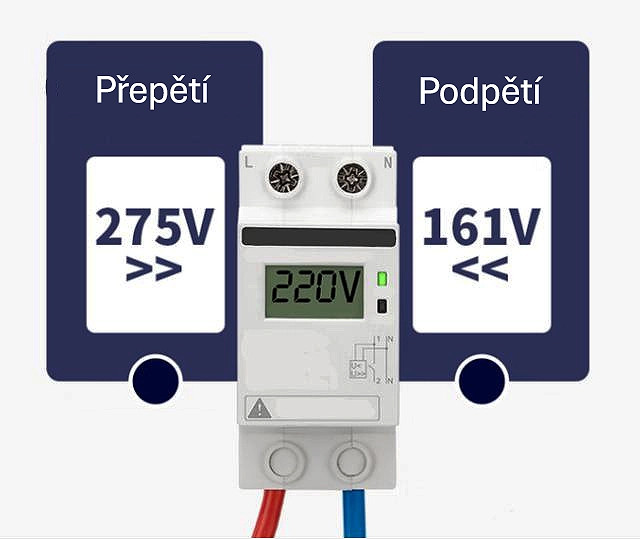
- 2. Overvoltage or Undervoltage in the Power Supply: The inverter is sensitive to unstable voltage. Sudden voltage spikes or drops can damage internal components, particularly the DC bus capacitors, which are critical for stable operation.
- 3. Failures of Output IGBT Transistors: These are the most common failures leading to inverter outages. They can be caused by motor overload, insulation faults, or incorrect parameter settings.
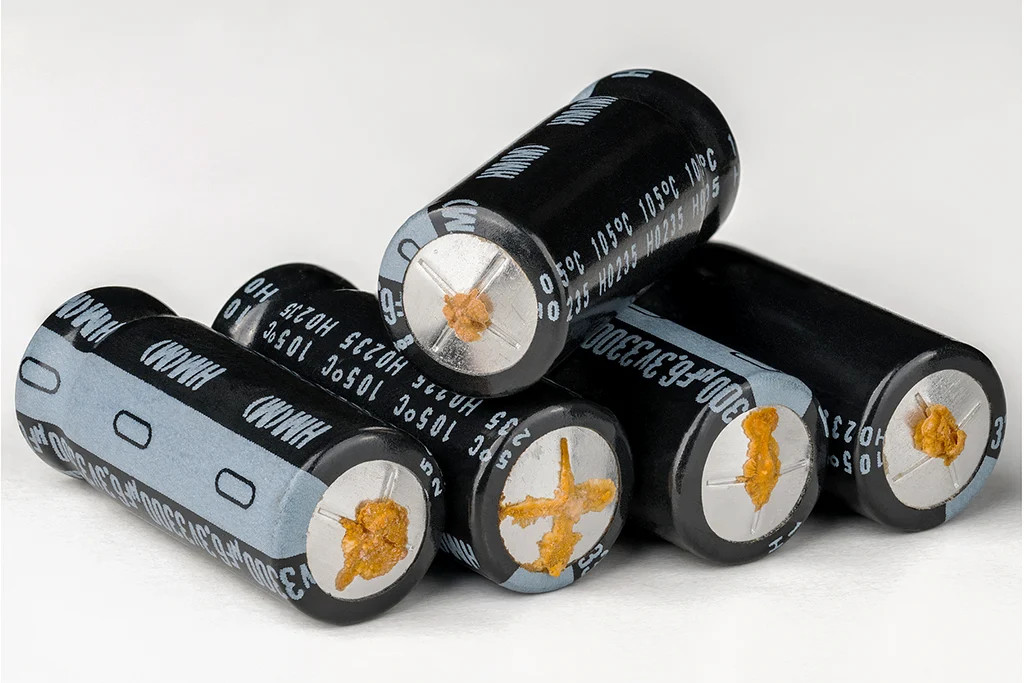
- 4. Failures of DC Bus Capacitors: These capacitors are used to smooth voltage and store energy. Their failure is common in older inverters or in environments with high operating temperatures, which significantly shortens their lifespan.

How to Prevent Failures
Prevention is key. Investing in simple and systematic maintenance can save you significant costs and unexpected headaches. Here are a few key steps:
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly clean the fans and heat sinks to ensure proper cooling. Check the cabinet for tightness to prevent dust and moisture from entering.
- Monitor Key Parameters: Monitor the operating temperature of the inverter and the motor, as well as the input and output voltage and current. Early detection of unusual values can prevent major failures.
- Correct Installation: Ensure the inverter is installed correctly according to the manufacturer's instructions. Use appropriate cables, fuses, and protection devices to ensure a stable and safe power supply.
- Operator Training: Train your operators on the correct and safe use of the VFD. A well-informed operator can often identify early warning signs of a problem.
- Avoid Overloading: Ensure the inverter is not consistently operating at or above its maximum rated load. Overloading can cause damage and significantly shorten the lifespan of its components.